People often come across various terms and names related to fuel system components like the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel injector, fuel injection pump, and fuel common rail system.
These are some of the terms that one would hear from a professional mechanic while inspecting your car for hard starting problems or maybe a car breakdown kind of situation.
The above-said fuel system components play a major role in ensuring the fuel reaches the engine for firing cylinders to keep your vehicle going.
Malfunctioning in any of the parts would mean that you should be ready to get your hands dirty! (If you are a DIY kind of person)
Since there are several parts involved, people often get confused between fuel system components, especially the one between the fuel injector and the fuel pump.
If the fuel pressure at the fuel pump outlet is within specifications as per the owner’s manual then the issue would be with the clogged fuel injectors sitting near the engine. If the fuel pressure is the problem, then you need to troubleshoot the fuel pump, sometimes it doesn’t get power at all.
If you want to know more details of the fuel injector and fuel pump, then you are at the right place.
Here in this article, we will specifically explain Fuel Injector Vs Fuel Pump and what differentiates one from the other.
Table Of Contents
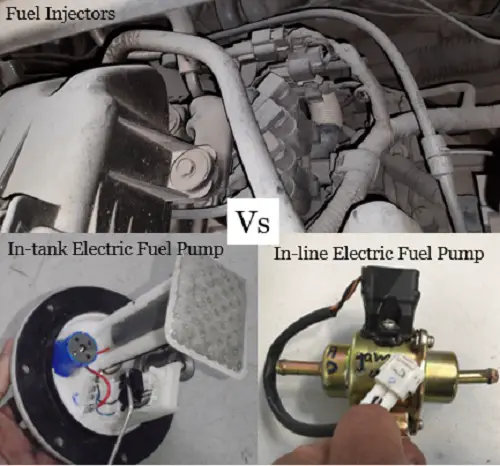
Fuel Injector
There are various fuel system components involved in keeping the vehicle running.
It starts from the fuel tank which stores fuel inside the fuel tank to ensure good mileage of the vehicle.
Then comes the fuel pump which supplies pressurized fuel to the engine through the fuel supply hoses.
The fuel then reaches the fuel injectors for firing the cylinders for vehicle running.
There are different types of fuel injectors being used in car engines but all serve the same purpose of injecting high pressure fuel inside the engine cylinders to participate in fuel combustion to crank the engine.
So here we are going to talk about details of fuel injector which is one of the major fuel system components and later discuss about the fuel pump to compare Fuel Injector Vs Fuel Pump back to back.
Function
The function of the fuel injector is to ensure fine atomization of the fuel which would get sprayed inside the engine cylinders to ensure complete combustion of the fuel.
The fuel injector usually has multiple super-fine holes on its injecting tip to achieve fine atomization of fuel.
The fuel injector doesn’t do anything on its own, it’s just to restrict the pathway of the fuel to generate fine atoms of fuel to ensure the stoichiometric ratio of the air-fuel mixture (14.7:1).
Location
In the case of the throttle body or port injection, the fuel injectors are located on the throttle body at some desired angles to ensure precise fuel throw.
But in the case of multi-point fuel injection (MPFI), the fuel injectors are located immediately on the back of intake valves of engine cylinders.
If you take direct injection vehicles, the fuel injector is located such that the fuel is sprayed directly into the engine cylinders past the intake valves for low emission and complete combustion of fuel.
Activation condition
The fuel injector opening holes are normally closed otherwise they would flood the engine cylinders.
Whenever the fuel injectors get the input signal from the ECU, it gets opened and sprays finely atomized fuel inside the cylinders.
The fuel injectors are duty cycle operated whose activation is controlled by the signal from the vehicle’s Electronic Control Module (ECU) (akka ECM (Engine Control Module), PCM (Powertrain Control Module)).
Fuel injectors generally have got coil arrangement to activate it. When the ECU sends a current pulse signal to the coils, it gets energized and the needle within it gets pulled up and this allows fuel to squirt into the manifold or engine cylinders.
The quantity of fuel allowed to pass through the injector is controlled by the strength and duration of the pulse signal which depends on fuel demand.
The vehicle ECU gets multiple inputs from the vehicle system components like throttle position sensor, speed sensor, and coolant temperature through which it comes to know the precise fuel demand required by the engine.
Malfunction Outcome
The possible failure mode of the fuel injectors would be clogging of injector holes.
This prevents fuel delivery to the engine. This may be due to the entanglement of foreign particles inside the fine holes on the injector’s spraying tip.
Typically, the source of foreign particles are via. contamination of the fuel tank or contaminants entering the fuel tank along with the fuel from the fuel pumping stations.
Unless the fuel injector is replaced with a new one, you may face issues like engine misfire, rough engine idle, engine hesitation during acceleration, vehicle starting problem, poor throttle response, and engine emission failure.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is an important part of the fuel system. Its key function is to ensure fuel is fed to the engine with the required fuel flow rate at desired pressure through the fuel supply lines.
Here we will elaborately discuss on fuel pump so that all your queries related to fuel injector Vs fuel pump will get answered.
There are various types of fuel pumps being used in a vehicle like an in-tank fuel pump, external fuel pump or lift pump, and high pressure fuel pump. All these pumps serve the same function of ensuring fuel delivery to the engine from the fuel tank.
Function and Location
In-tank fuel pump

The in-tank fuel pump is usually located on the top of the fuel tank which is mounted below the underbody floor panel of the vehicle. Fuel pump is submerged inside the fuel in the tank.
The main function of an in-tank fuel pump is to suck fuel from the fuel tank and feed it upstream to the engine at some desired pressure (say 3 bar).
In the case of gasoline vehicles, the in-tank fuel pump pressurizes fuel to ensure fine atomization of fuel at fuel injectors and there is no additional high pressure fuel pump required.
The in-tank fuel pump usually has got fuel strainer, electric motor, pressure regulator, and a non-return check valve.
The fuel pump has got impellers in case of centrifugal type pump that sucks fuel through the strainer on the suction side to filter out the contaminants and generates pressure on the discharge side and delivers clean pressurized fuel to the engine via. fuel hoses.
The fuel pump usually has a pressure regulator to regulate the pressure at which the fuel is being fed to the engine. Any excess pressure developed would be leaked back into the fuel tank through return hose.
In-Line fuel pump or Lift pump

Diesel vehicles have an inline external fuel pump or lift pump which serves the same purpose as an in-tank fuel pump.
It only picks up fuel from the fuel tank and supply it to the engine and has little participation in developing the high pressure required for the fuel injection.
The lift pump is located externally on the chassis of the vehicle by bolting arrangement and not on the fuel tank.
In the case of an external in-line fuel pump, the fuel is pumped either by the reciprocating or centrifugal action.
High pressure fuel pump
In the case of diesel vehicles, in addition to the lift pump, the engine has high pressure fuel pump mounted on the engine and driven by the engine through a drive shaft arrangement.
This high pressure fuel pump has a vane-type fuel pumping arrangement capable of developing pressures exceeding 2000 bar.
As the fuel pump’s drive shaft rotates, the vane pump rotor is rotated. This creates vacuum and draws the fuel from the fuel tank and delivers it to the fuel injectors or common rail system at high pressure.
The outlet of the vane pump is controlled by the metering valve which in turn is controlled by the throttle response mechanism through governor weight retainer arrangement.
At the start when the engine RPM is low, the governor weight retainer ensures that the metering valve is closed and negligible fuel is supplied to the engine.
As the fuel demand increases when the throttle is opened gradually (via. accelerator pedal input) and the engine RPM increases, the governor retainer opens the metering valve and allows more fuel supply from the vane pump to the engine’s fuel injectors.
The fuel which is pumped by the high pressure fuel pump is sent to the common rail system wherein the fuel is delivered into multiple ports situated on the back of the intake valve of the cylinders and reaches the fuel injectors.
Activation condition
In-tank and External Fuel Pump
The fuel pump gets the signal from the ECU that allows the power supply to the fuel pump depending upon the car key position (Ignition ON or START).
This activates the motor of the fuel pump and pressurized fuel starts flowing out of the outlet nozzle of the fuel pump.
Usually, when the car key is kept in the ignition position, ECU grounds the fuel pump and supply power to it, to run the fuel pump for 3 seconds, and then it stops.
In the case of a gasoline engine, this 3 sec allows priming of the fuel pump to ensure that the fuel supply line is always kept under pressure and the pressurized fuel is readily available at the back of fuel injectors for fuel injection.
This makes sure that the vehicle starts immediately when the engine is cranked (key in START position). Otherwise, more no. of cranks will be required to build pressure in the fuel hose.
High Pressure Fuel Pump
In the case of a diesel engine, the fuel pump is driven by the engine through a drive shaft mechanism.
The drive shaft of the fuel pump is driven by the engine through governor weight retainer and fuel metering arrangement which in turn is controlled by the accelerator throttle response.
Malfunction outcome
In-tank fuel pump
The in-tank fuel pump usually functions fine as long as there is no entanglement of foreign particles inside the suction strainer or impeller bucket blades.
Since the strainer is generally located close to the fuel tank bottom surface where the foreign particles get settled, there is a large possibility of the strainer sucking dust particles and clogging itself.
Clogging of the strainer reduces the fuel flow rate and creates a large pressure drop across the strainer resulting in low delivery pressure of fuel.
An impeller is generally sandwiched between inlet/outlet plates. The presence of the foreign particles wears the impeller surfaces and increases the gap between the impeller blades and the inlet/outlet plates.
This also drastically reduces the fuel flow rate and the discharge pressure which results in engine misfire, engine sputtering while acceleration, poor throttle response and even vehicle break down unless the fuel pump or strainer is replaced with a new one.
You may like to read “Fuel Pump Primes But No Pressure. Everything You Need To Know!“
External fuel pump Or Lift pump
Symptoms of malfunction of the lift pump are similar to that of an in-tank fuel pump, the only difference being, the fuel filters will relatively pick up less dust particles that gets settled inside the fuel tank comparing to that of an in-tank fuel pump.
The particles which are suspended in the fuel may get entangled but not the one which get settled at the tank bottom.
But in the case of an external lift pump, since it is not submerged inside the fuel, the heat dissipation rate is much lower than the in-tank fuel pump wherein the fuel pump is cooled off by the fuel inside the fuel tank.
This heat reduces the durability life of the fuel pump and causes vehicle starting problems, and poor throttle response over some period of running. It is recommended to replace the lift pump with a new one, if you face vehicle driving issues.
High pressure fuel pump
Since the high pressure fuel pump gets its fuel either from the external lift pump or in-tank fuel pump, it is the latter that needs frequent maintenance and replacement.
The high pressure fuel pump owing to its general durability life and wear and tear may lead to fuel supply problems as the vehicle ages and resulting in engine misfire, poor throttle response, and vehicle hard starting issues.
The high pressure fuel pump usually lasts for the life of the vehicle and may need replacement with a new one very rarely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a bad fuel pump cause injector problem?
Yes, why not! Once the fuel pump strainer is clogged, it would start sending unfiltered fuel along with dust articles to the fuel injectors and thereby clogs the injector nozzle holes.
Forget about the atomization of the fuel, the fuel injectors won’t even deliver fuel across it, once the injectors outlet holes are clogged. This leads to fuel injector-related issues in vehicle as discussed earlier.
How do I know if my fuel pump or fuel injector is bad?
Take out the fuel pump and connect the outlet nozzle of the fuel pump to a pressure guage by a fuel hose and T-connector arrangement and block the free end of the hose.
Supply power to the fuel pump electrical connectors. You shall be able to measure the block condition or shut-off pressure of the fuel pump on the pressure gauge.
If the readings are within the specifications as per the vehicle manufacturer, then the problem lies in the fuel injectors or any other engine component and not the fuel pump.
If the fuel injector seems to be working fine, then it is possible that the fuel pump is not getting power.
If you don’t have a pressure gauge, simply check the pressure of the fuel at the pump outlet by pressing the thumb on the outlet nozzle.
You should be able to feel the fuel pressure on your thumb, otherwise, the fuel pump is the culprit. Of course you should have judgement of sensing fuel pressure!
Does fuel injection require a fuel pump?
Yes, the fuel pump is required to develop high fuel pressure which is essential for fine atomization of fuel at the fuel injector.
Since the fuel pump is located beneath the floor panel of the vehicle, the fuel inside the fuel tank has to be taken from the tank’s lower position to the engine’s higher position.
The fuel pump apart from lifting the fuel to a higher location, also develops pressure in the case of a gasoline engine which is necessary for fuel atomization.
Fuel pump is not required in the case of a carburetor engine where the gravity feed would suffice, if the fuel tank packaging position ensures positive potential head above the engine.
Conclusion
Fuel injectors and fuel pumps play a major role in the working of the engine and ensure proper vehicle running. Owing to its terminology, people most often confuse one for another or could not differentiate the functions performed by these components.
From the discussions so far, you may be able to understand that the fuel injectors don’t generate high pressure fuel which is the function of the fuel pump.
Fuel injectors merely help in finely atomizing the fuel for complete fuel combustion by restricting the pressurized fuel flow path across spray holes.
The pressurization of the fuel is the role of the fuel pump and not the fuel injectors. Fuel supply hoses transfer the pressurized fuel from the fuel pump up to the injectors.
Whenever there is a malfunction of either fuel injectors or fuel pump, you are bound to get vehicle-related problems and the concerned parts needs to be fixed before it creates havoc.
Hope from the above comparison of Fuel Injector Vs Fuel Pump, you would be able to figure out what is the function of fuel injector and fuel pump, where it is located, activation conditions, and malfunction outcomes, etc.,
Since there is a huge difference in the way in which both the fuel injectors and fuel pump works, it is easy to troubleshoot the issues related to these parts and identify the root cause for the underlying problems associated with them.
Happy motoring!
Related Articles
Fuel Pump Vs Fuel Filter? How to Identify Problems?
Fuel Pump Primes But No Pressure? Everything You Need To Know!
Fuel Pump Not Priming? Reasons And Solutions To Fix It!
Car Won’t Start After Fuel Pump Replacement. All You Need To Know!
Fuel Pump Runs Continuously With Key On? (9 Causes And Solutions To Fix It!)