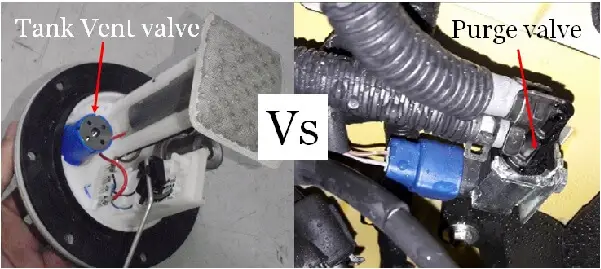
If you have a car that is approximately 30 years old and runs on gasoline fuel, then probably you must be aware of the evaporative emission control system (EVAP) fitted in your vehicle.
This EVAP system involves several valves namely the fuel tank vent valve, pressure switching valve, canister vent valve (solenoid), and purge valve (solenoid)
These valves are required to perform evaporative emission control functions, starting from relieving the fuel vapors from the fuel tank, collecting those gas vapors in the charcoal canister, and consuming the stored vapors in the engine for combustion.
Since there are several valves involved, people often get confused between the valves.
These valves play an important role in the function of the EVAP system, it is essential to get the basics right to understand the EVAP system.
If you are also confused about the use of different valves and their terminology, then you are at the right place. Here in this article, we will specifically explain Vent Valve Vs Purge Valve, in which people frequently end up mixing one valve for the other.
Table Of Contents
Vent valve
Generally, two vent valves are used in any EVAP system. One is the fuel tank vent valve and the other one is the charcoal canister vapor vent valve (solenoid).
So here we are going to talk about both vent valves back to back to understand their importance.
Function
Canister vent valve
The function of the canister vent valve is to prevent pressure or vacuum build-up inside the fuel tank which is caused by a lot of factors like increase or decrease in gasoline temperature, fuel consumption, fuel sloshing inside the fuel tank, etc.
Thus its main role is to maintain the atmospheric pressure inside the fuel tank to prevent undue load on the fuel system parts.
Fuel tank vent valve
The fuel tank vent valve is also known as the roll-over valve, hence there is less tendency to get confused with the canister vent valve. So there will not be any question of Vent Valve Vs Purge Valve. Isn’t it?
As the name indicates, the main role of the roll-over valve is to prevent liquid fuel from entering the charcoal canister in the event of vehicle toppling and also to facilitate vapor movement to the charcoal canister.
Location
Usually, the charcoal canister vent valve is located on the top of the charcoal canister. Sometimes it is mounted by a bracket arrangement to the vehicle body and connected to the open port of the canister by a hose on one side and kept open to the atmosphere on the other side.
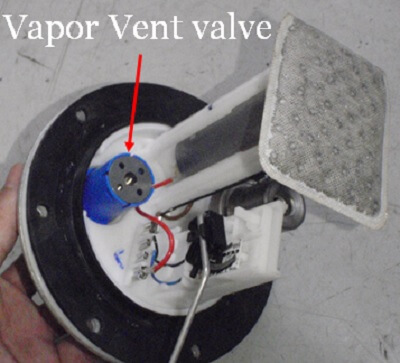
On the other hand, the fuel tank vent valve is located on the top of the fuel tank and sometimes it comes inbuilt with the in-tank fuel pump module.
Number of ports
When the canister vent valve is mounted on top of the canister, it has only one port that is open to the atmosphere.
Similarly, the fuel tank vent valve usually has only one port and is connected by a hose to the charcoal canister.
Valve condition (open or close)
The canister vent valve is normally open to the atmosphere. When the pressure develops inside the fuel tank, this allows the escape of hydrocarbon-free air to the environment and adsorbs hydrocarbon vapor over the charcoal particles.
On the other hand, the canister vent valve also allows the atmospheric air to pass across the canister and into the fuel tank to offset the vacuum which would get generated inside the fuel tank after fuel consumption or fuel temperature drop.
Activation condition
When the EVAP Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) system performs a large and small leak integrity test, the canister vent valve gets activated by the signal from the vehicle electronic control unit (ECU).
This closes the canister vent valve and prevents the communication of the EVAP system with the atmosphere.
Large and small leak tests are large vacuum application and vacuum decay test which is performed by keeping the purge valve open in the former and closed in the latter test.
These tests are monitored by the fuel tank pressure sensor which gives feedback to the vehicle ECU to indicate whether the test is passed or not.
The fuel tank vent valve is normally closed but it opens when the pressure inside the fuel tank exceeds approximately 8 to 10 inches of H20. This is to maintain the fuel tank under certain desired pressure to reduce the formation of fumes from gasoline. In some of the old vehicles, it may be an open valve all the time.
Malfunction Outcome
When we talk about the malfunction of the canister vent valve, it means it is either stuck closed or stuck open.
If it is stuck closed, the fuel system venting will be blocked and there will be pressure or vacuum generation inside the tank which would affect in-tank fuel pump operation and the gas tank overflows when filling.
This will cause engine hesitation, vehicle starting problems, difficulty in filling the fuel tank, loud noise coming from the fuel tank or fuel cap, engine emission failure, and will get diagnostic error codes in case of EVAP venting integrity test.
The above issues apply to the fuel tank vent valve as well in the event it is stuck closed.
On the other hand, if the canister vent valve is stuck open, you will notice the check engine light (CEL) on the dashboard and will also get the P0447 diagnostic error code and the vehicle will not pass the smoke test.
If the fuel tank vent valve is stuck open, then the gas fumes would be constantly sent to the charcoal canister and probably there will be more fumes generation inside the fuel tank but there won’t be major drawbacks.
Purge valve
The purge valve is an important part of the EVAP system. Its key function is to pull away or purge the vapors collected in the charcoal canister towards the intake manifold for engine combustion.
There are various features in the purge valve which differentiate it from the vent valve.
Location
The Purge valve is usually located close to the engine intake manifold sitting next to the throttle body. The other location is over the fuel tank and sitting on top of the charcoal canister.
Number of ports
The purge valve has two ports, one for the inlet of vapors coming from the charcoal canister and the other is for the outlet to the engine intake manifold. The two ports are connected through a plunger seal arrangement.
Valve condition (open or close)
The purge valve is normally closed. It opens only when it is activated by the ECU under certain favorable conditions.
When it opens, the engine intake vacuum would be applied to the charcoal canister for purging the vapors towards the engine for combustion which otherwise would saturate the canister and escape through canister vent ports.
Activation condition
If the purge valve is endlessly kept open, it would be constantly allowing vapor and air toward the engine.
This would affect the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio of the mixture which would be getting burnt in the engine at idling and may lead to engine emission failure.
So the purge valve has to be in operation only under certain conditions which will be favorable to the engine. All the circumstances mentioned below shall be satisfied for the purge valve to open.
- Engine coolant shall be above the threshold temperature limit (say 185◦ F)
- Percentage throttle opening shall exceed certain values (say after 5%). Remember that the purge inlet nozzle on the intake manifold is located just behind the throttle body butterfly valve.
- The exhaust oxygen sensor shall give an output signal as 1 to ECU. This ensures closed-loop feedback about the oxygen percentage to estimate the air-fuel ratio being burnt in the engine.
- Engine RPM reaches above 1000.
In modern vehicles having an onboard diagnostic (OBD) system, when the ECU checks the evap system for integrity, especially during the large leak test (vacuum generation test), the purge valve will be kept open and during the small leak test (vacuum decay test), the purge valve is signaled to be kept closed.
Malfunction Outcome
As in the case of the canister vent valve, here also malfunction would mean the purge valve is either stuck closed or stuck open.
If the purge valve is stuck closed, the charcoal canister would not be purged. This would cause hydrocarbon saturation of the canister and thereby the charcoal canister gets filled with gas.
The above event would cause clogging of charcoal canister ports and the fuel system venting would be blocked. Hence this will cause the same issues as mentioned above in the case of vent valve stuck closed condition.
Besides, it will have a gas smell issue since the gas fumes would be escaping through the canister opening ports to the atmosphere, and creates air pollution and fire hazard risk. Hence this will also result in less fuel economy.
On the other hand, if the purge valve is stuck open, it would mean there will be constant purging and would affect the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio at idling conditions and may fail the engine emission test.
You may try cleaning the purge valve, if it is the case of a stuck closed/open issue and check whether the symptoms of a bad purge valve disappear.
In other driving conditions like partial or wide-open throttle, it may lead to uncontrolled acceleration and engine rev up issues.
Also, you will notice CEL on the dashboard and will also get the P0444 diagnostic error code and the vehicle will not pass the smoke test as well.
Conclusion
Both vent valve and purge valve plays an important role in performing the functions of the EVAP system.
Whenever there is a malfunction in any of the valves, it has to be fixed before it damages other parts of the vehicle.
Otherwise, it becomes an expensive affair, and many times you may need to spend an extensive amount of time finding the root cause of the problems.
Hope from the above comparison of Vent Valve Vs Purge Valve, you would be able to figure out what is the function of vent and purge valves, where it is located, activation conditions, malfunction outcomes, etc.,
Since there is a vast difference in the way in which both the vent and purge valves function, it is easy to troubleshoot the issues related to these valves and identify which valve is the root cause of the underlying problems associated with it.
Related articles
Charcoal Canister Delete? Everything you need to know!
Can You Bypass Evap Purge Valve? Let’s know the facts!
Can You Bypass Charcoal Canister? Let’s Find Out!
Can Purge Valve Be Cleaned? Everything You Need To Know!
Gas Tank Overflows When Filling? All You Need To Know!
Charcoal Canister Filled With Gas? Ways To Fix!